Computers, like any sophisticated machinery, have a heartbeat that’s often gauged by the CPU’s temperature. It’s a critical metric indicative of your system’s health and efficiency.
The CPU, being the brain of your computer, needs to operate within a safe temperature range to prevent overheating, which can lead to reduced performance or even hardware damage.
In Windows 11, monitoring CPU temperature isn’t just a technical task; it’s a necessity for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your machine. Today, I will explain how to check the temperature of your processor on Windows 11.
First Things First
To appreciate the importance of monitoring CPU temperature, one must understand what constitutes a normal range. Typically, a processor should run between 30°C to 70°C under moderate usage. However, during intense activities like gaming or video editing, temperatures can spike.
It’s when these numbers cross the threshold of 80°C to 90°C that you should be concerned, as prolonged exposure to high temperatures can degrade CPU performance and lifespan.
Tools and Techniques for Monitoring
Windows 11 doesn’t include a native feature to check CPU temperature directly. However, there are reliable third-party applications and BIOS methods to accomplish this. The choice of tool depends on your comfort level with technology and the depth of information you require.
These range from simple software solutions to more detailed system analysis tools that provide comprehensive insights into your CPU’s performance and health.
Third-Party Software Options
User-Friendly Software Solutions
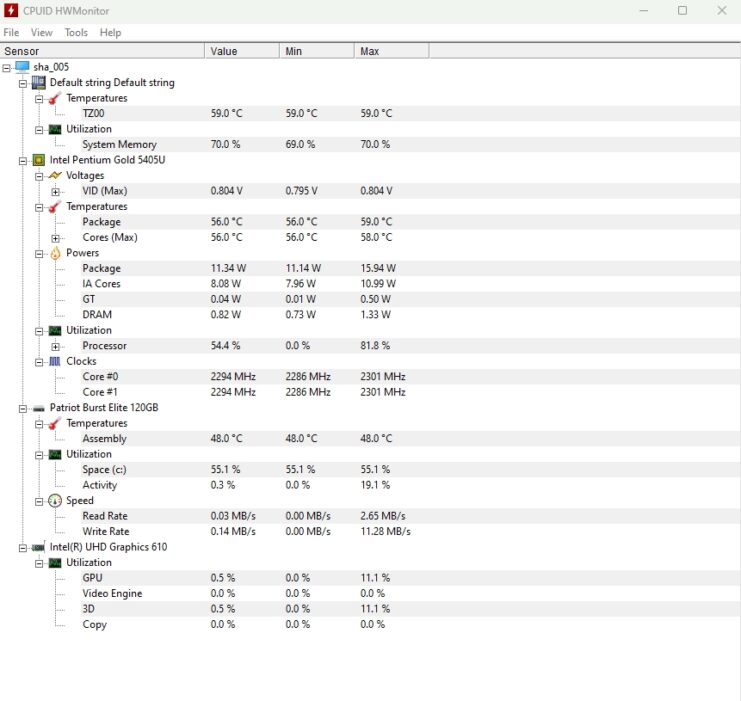
- HWMonitor: A popular choice for its user-friendly interface. It provides real-time monitoring of CPU temperature, voltage, and fan speed.
- Speccy: Offers detailed information about your system’s hardware, including temperature readings for each CPU core.
- Core Temp: A lightweight tool specifically designed for temperature monitoring. It displays data for each core and can provide real-time alerts.
Advanced System Analysis Tools
- AIDA64 Extreme: An advanced system diagnostic tool that provides detailed hardware analysis, including temperature.
- Open Hardware Monitor: An open-source tool that offers a broad range of system information, including CPU temperature.
BIOS-Based Monitoring Methods
For those who prefer a hands-on approach, checking the CPU temperature through the system’s BIOS is an option. This method provides basic temperature readings and doesn’t require any additional software installation.
However, it’s less convenient than software solutions and doesn’t offer real-time monitoring while using Windows.
Step-by-Step Guide to Monitoring CPU Temperature
Installing and Using HWMonitor
- Download and Install: Visit the official HWMonitor website, download the software, and follow the installation instructions.
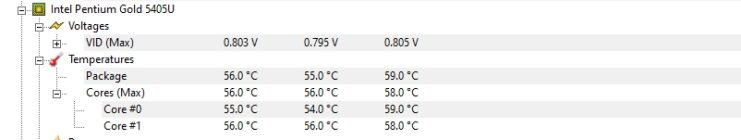
- Launch and Analyze: Open HWMonitor. It will display a list of hardware components. Locate the processor and observe the temperature readings.
- Understanding the Readings: HWMonitor provides current, minimum, and maximum readings for each core, allowing you to identify any overheating issues.
Utilizing Core Temp for Detailed Insights
- Installation Process: Download Core Temp from its official website and install it.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Launch Core Temp to view real-time temperature readings for each CPU core.
- Setting Up Alerts: Core Temp allows you to set temperature alerts, which can be useful to prevent overheating during intensive tasks.
Accessing BIOS for Monitoring
- Reboot into BIOS: Restart your computer and press the BIOS key (often F2, F10, DEL, or ESC) as it boots.
- Navigating BIOS: Look for a section labeled ‘PC Health Status’ or ‘Hardware Monitor’. Here, you’ll find the CPU temperature.
- Limitations: Remember, BIOS won’t provide real-time monitoring while you use Windows 11.
Best Practices for Maintaining Optimal Temperature
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
- Dust Removal: Regularly cleaning your computer’s interior, especially the fans and heat sinks, can significantly improve cooling efficiency.
- Thermal Paste Application: Cleaning and reapplying thermal paste every few years ensures better heat conduction between the CPU and its cooler.
Upgrading Cooling Systems
- Better Fans: Upgrading to higher-quality fans can enhance air circulation.
- Liquid Cooling Systems: For high-performance PCs, liquid cooling systems offer superior cooling capabilities compared to traditional air cooling.
Optimizing Computer Usage
- Balancing Workload: Avoid running too many intensive applications simultaneously.
- Environmental Considerations: Ensure your computer is in a well-ventilated area and not exposed to high ambient temperatures.
Common Issues

Identifying Overheating Symptoms
When a CPU overheats, it often exhibits several telltale signs:
- System Crashes and Blue Screen of Death (BSOD): Frequent system crashes can be a red flag for CPU overheating.
- Slow Performance: If your computer starts to lag or run slower than usual, it might be struggling with high temperatures.
- Noisy Fans: When your CPU gets too hot, the fans work harder to cool it down, resulting in increased noise.
Troubleshooting Overheating Problems
- Check Airflow: Ensure your computer’s air vents are not blocked and that there’s adequate airflow around the case.
- Update Software and Drivers: Outdated drivers or software can cause your CPU to work harder than necessary, leading to increased temperatures.
- Consider a Hardware Check: If the problem persists, it might be time to check if the cooling system is functioning correctly or if the thermal paste needs reapplication.
Preventive Measures
- Routine Maintenance: Regular cleaning and maintenance of your PC can prevent many overheating issues.
- Balanced Usage: Avoid overloading your CPU with too many tasks simultaneously, especially for prolonged periods.
Advanced Tips for Tech Enthusiasts
1. Monitoring CPU Temperature Using Command Line
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, Windows PowerShell can be used to check CPU temperature, although it’s more complex than using third-party software.
2. Automating Alerts with Task Scheduler
Setting up Task Scheduler to alert you when CPU temperatures reach a certain threshold can be a proactive way to prevent overheating. This requires some technical know-how but can be a valuable tool for power users.
3. Know About the Impact of Overclocking
Overclocking your CPU can significantly affect its temperature. While it boosts performance, it also increases heat output, making efficient cooling even more critical. Be mindful of the risks and ensure your cooling system can handle the extra heat.
FAQs
Can high ambient room temperature affect my CPU’s temperature?
Yes, the ambient room temperature can significantly impact your processor’s temperature. A warmer environment means your computer’s cooling system has to work harder to dissipate heat, which can lead to higher processor temperatures.
It’s advisable to keep your computer in a cool, well-ventilated area to help manage temperatures effectively.
How often should I check my processor temperature?
The frequency of checking it depends on your usage. If you use your computer for basic tasks, checking every few months is sufficient.
However, if you engage in CPU-intensive activities like gaming or video editing, or if you live in a hot climate, it’s a good idea to check more frequently, perhaps weekly or bi-weekly.
Can updating my operating system impact CPU temperature?
Yes, operating system updates can impact it. Updates often include optimizations that can make your system run more efficiently, potentially reducing CPU workload and heat.
Conversely, some updates might initially increase CPU usage due to new processes or features, temporarily affecting temperature.
Are there any warning signs that my CPU is overheating besides temperature readings?
Besides these readings, signs of an overheating CPU include system instability, random reboots, performance throttling, and, in extreme cases, physical signs like a hot-to-the-touch case or a burning smell from the computer.
Can I use Windows Task Manager to monitor CPU temperature?
No, Windows Task Manager does not provide these readings. To monitor the temperature, you’ll need to use third-party software, such as HWMonitor, Core Temp, or check through your system’s BIOS.
Does CPU temperature affect the overall lifespan of a computer?
Yes, consistently high temperatures can shorten the lifespan of not only the processor itself but also other components in your computer.
High heat can lead to thermal stress, causing components to wear out more quickly. Proper temperature management is key to maintaining the health and longevity of your PC.
Final Words
Monitoring your CPU temperature is not just about avoiding immediate damage; it’s about ensuring the longevity and reliability of your PC. With the right tools and knowledge, you can keep your system cool under pressure, guaranteeing optimal performance and a longer lifespan for your hardware.
Whether you’re a casual user, a gaming enthusiast, or a professional, understanding and managing your processor temperature is a key aspect of maintaining your computer’s health and performance.
Remember, staying informed and proactive about your CPU temperature is not just about solving issues as they arise but also about preventing them in the first place. With the evolving landscape of processor temperature management, staying ahead of the curve ensures that your Windows 11 experience remains smooth, efficient, and cool.